Top 3 biggest mosque in the world
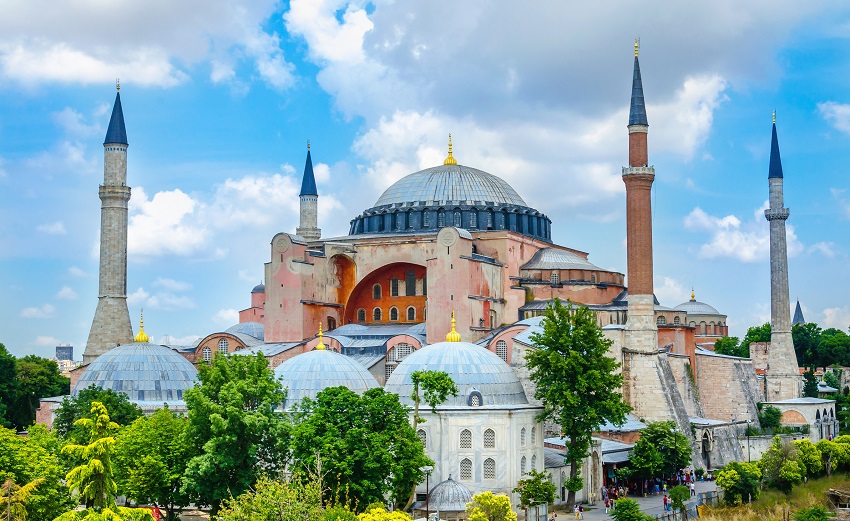

Masjid al-Haram,
Masjid al-Haram, also known as the Great Mosque of Mecca, is the most sacred and significant mosque in Islam. Located in the city of Mecca, Saudi Arabia, it surrounds the Kaaba, which is the holiest site in Islam. Here's some information about Masjid al-Haram:

-
Importance: Masjid al-Haram holds immense religious significance for Muslims around the world. It is considered the House of Allah and is the focal point of the Hajj pilgrimage, which is one of the Five Pillars of Islam. Muslims face towards the Kaaba during their daily prayers, symbolizing the unity of the Muslim community.
-
Kaaba: At the center of Masjid al-Haram stands the Kaaba, a cubic structure draped in a black cloth called the Kiswa. Muslims believe that it was built by the Prophet Ibrahim (Abraham) and his son Ismail (Ishmael) as the first house of worship dedicated to Allah. The Kaaba is believed to be the earthly dwelling place of Allah and is the direction towards which Muslims worldwide pray.
-
Expansion and Architecture: Over the centuries, Masjid al-Haram has undergone several expansions to accommodate the increasing number of pilgrims. The current structure covers an area of approximately 356,800 square meters and can hold millions of worshippers. The mosque's architecture combines traditional and modern elements, with its most distinctive feature being the large, iconic clock tower called the Abraj Al-Bait.
-
Tawaf: Pilgrims visiting Masjid al-Haram perform a ritual called Tawaf, which involves circling the Kaaba seven times counterclockwise. During Tawaf, Muslims express their devotion and obedience to Allah, supplicate, and seek blessings. The circling of the Kaaba represents the unity of Muslims and their submission to Allah.
-
Zamzam Well: Located within the precincts of Masjid al-Haram is the Zamzam Well. According to Islamic tradition, it is a miraculous well that originated when the Prophet Ismail's mother, Hajar, desperately searched for water in the barren desert for her son. The well provides holy water that is highly regarded and consumed by pilgrims.
-
Hajj and Umrah: Masjid al-Haram is the destination for millions of Muslims who undertake the Hajj pilgrimage, which occurs during the Islamic month of Dhu al-Hijjah. Hajj is a mandatory act of worship for able-bodied Muslims who can afford the journey. Additionally, Muslims can perform Umrah, a lesser pilgrimage, at any time of the year.
-
Historical Significance: Masjid al-Haram has witnessed significant historical events. It has been renovated and expanded by various Islamic caliphs and rulers throughout history. The mosque has endured fires, floods, and natural disasters, but it has always been rebuilt and restored with utmost care and reverence.
It's important to note that access to Masjid al-Haram is restricted to Muslims only. Non-Muslims are not allowed to enter the mosque itself but can appreciate its grandeur from outside. Masjid al-Haram serves as a powerful symbol of unity, spirituality, and devotion for Muslims worldwide, and it holds a special place in the hearts of millions of believers.
Al-Masjid an-Nabawi,
Al-Masjid an-Nabawi, also known as the Prophet's Mosque, is one of the most significant Islamic sites located in the city of Medina, Saudi Arabia. It holds immense religious and historical importance as it was established by the Prophet Muhammad (peace be upon him) himself and serves as his final resting place.

Historical Background: The original mosque was a simple structure built by the Prophet Muhammad in the year 622 CE after his migration from Mecca to Medina. Over the centuries, it has undergone several expansions and renovations to accommodate the increasing number of worshippers.
Architecture: Al-Masjid an-Nabawi's architecture is a blend of modern and traditional Islamic styles. It covers a vast area of approximately 400,500 square meters and can accommodate hundreds of thousands of worshippers. The mosque's main features include the central courtyard (sahn), prayer halls, the green dome, and minarets.
The Green Dome: The Green Dome, located at the southeastern corner of the mosque, is one of its most recognizable elements. It covers the tomb of the Prophet Muhammad and is considered a symbol of the mosque. The dome's interior is adorned with beautiful Islamic calligraphy and intricate designs.
Courtyards and Prayer Halls: The central courtyard, known as the Rawdah or Riyad al-Jannah, is a sacred area within the mosque. It is believed to be a part of Paradise, and it is highly revered by Muslims. Pilgrims and visitors often gather in the Rawdah to offer prayers and seek blessings.
The mosque consists of multiple prayer halls, including the main prayer hall (Al-Suffah), women's prayer area, and other designated areas for men and women. The halls are designed with elaborate carpets, chandeliers, and intricate decorations.
Significance: Al-Masjid an-Nabawi holds immense spiritual significance for Muslims worldwide. It is the second holiest mosque in Islam, after the Masjid al-Haram in Mecca. It is highly revered because the Prophet Muhammad spent the last years of his life in Medina and delivered many of his sermons and teachings in this mosque.
Pilgrimage and Visitation: Muslims from around the world visit Al-Masjid an-Nabawi throughout the year, with a particular emphasis during the Hajj and Umrah seasons. Pilgrims often include a visit to the mosque as part of their religious journey.
Etiquettes and Practices: When visiting Al-Masjid an-Nabawi, visitors are expected to follow certain etiquettes and practices. These include being respectful, maintaining proper dress code, avoiding noise and disruption, and observing the sanctity of the mosque.
In recent years, the Saudi Arabian government has undertaken major expansion projects to accommodate the increasing number of pilgrims and enhance the facilities of the mosque. These projects have included enlarging the courtyards, constructing new entrances, and improving infrastructure.
Al-Masjid an-Nabawi stands as a symbol of Islamic heritage and serves as a unifying place for Muslims worldwide. It continues to be a center of worship, knowledge, and spiritual enlightenment for millions of Muslims who seek solace and connection with their faith.
Faisal Mosque,
Faisal Mosque is an iconic landmark located in Islamabad, the capital city of Pakistan. It is one of the largest mosques in the world and holds great significance in terms of architecture, religious importance, and cultural heritage.

Construction of the Faisal Mosque began in 1976 and was completed in 1986. The mosque was named after King Faisal bin Abdul Aziz of Saudi Arabia, who generously provided financial support for its construction. The mosque was designed by a Turkish architect named Vedat Dalokay and incorporates a fusion of modern and traditional Islamic architectural styles.
The design of the Faisal Mosque is inspired by a desert Bedouin's tent, with its unique triangular shape and four minarets standing tall at the corners. The mosque is constructed mainly with white marble and reflects a minimalist aesthetic. It can accommodate up to 100,000 worshippers, making it one of the largest prayer spaces in the world.
The interior of the Faisal Mosque is equally impressive. The main prayer hall is vast and features a simple yet elegant design. The walls are adorned with intricate Islamic calligraphy, and a large chandelier hangs from the center of the hall, adding to the mosque's grandeur. The open courtyard surrounding the mosque provides additional space for worshippers during peak times.
The Faisal Mosque holds a significant place in the hearts of the Pakistani people. It serves as a symbol of national pride and religious harmony. The mosque has become a popular tourist attraction, drawing visitors from around the world who come to admire its architectural beauty and experience its tranquil ambiance.
Apart from its religious significance, the Faisal Mosque also serves as an educational and cultural center. It houses a library, an Islamic research center, and an auditorium for lectures and seminars. The mosque complex also includes a museum that showcases Islamic art, calligraphy, and historical artifacts.
Overall, the Faisal Mosque stands as a remarkable testament to Pakistan's rich cultural heritage and its commitment to Islamic architecture. Its striking design, serene atmosphere, and cultural significance make it an architectural marvel and a must-visit destination for tourists and worshippers alike.